
The epoch (point in time) of 1950 was mostĬommonly used during the middle to late part of the 20th century. Because of this precession and other related but smaller effects, astronomers convert the observed positions at any one instant into one appropriate for a convenient point in time so that locations can be more easily compared. The starting point (0 degrees = 0 hours) is currently in the constellation of Pisces but is moving slowly although constantly (it takes about 26,000 years to make a complete circuit the major component of this motion is called the "precession of the equinoxes"). It is measured in either degrees (0 to 360) or in hours, minutes and seconds (00h00m00s up to but not including 24h00m00s). Right ascension is analogous to longitude on the earth's surface.

The Big Ear radio telescope can observe in the 100-degree range of declination from approximately -36 degrees to approximately 64 degrees. Its range of values goes from -90 degrees (at the south celestial pole) through zero (on the celestial equator) up to +90 degrees (at the north celestial pole). Declination is the angular distance above or below the projection of the earth's equator onto the celestial sky. The next two groups of numbers on the computer printout (just to the right of the center of the row) are the right ascension and declination converted to epoch 1950.
#Seti wow code#
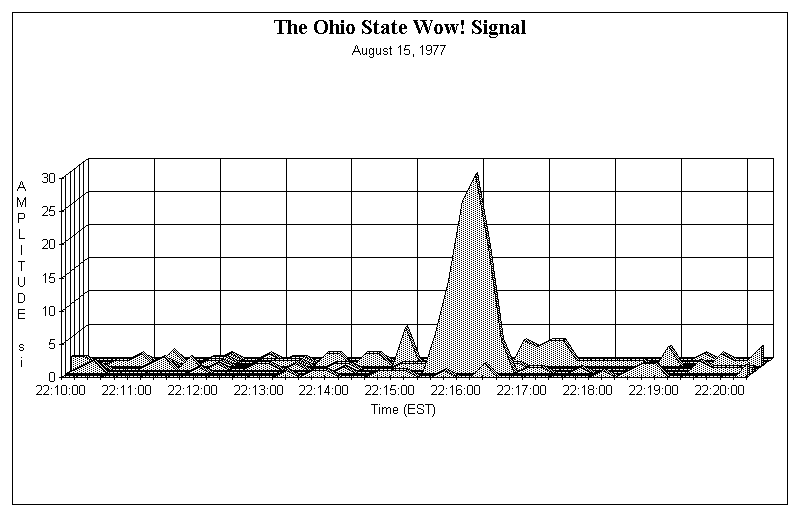
Thus, the "6EQUJ5" code in channel 2 means successive intensities as follows: 6 -> the range 6.0 - 6.999. They used a system of only one alphanumeric character to denote the signal strength. Each of the first 50 columns of the computer printout shows the successive values of intensity (or power) received from the Big Ear radio telescope in each channel (10 kHz wide) in successive 12-second intervals (10 seconds was used for actual sampling and another approximately 2 seconds was needed for computer program. It involved a short duration high energy pulse. Originally designed by Point & Click Software, Inc.On August 15, 1977., SETI received a 1 shot signal that many have described as a WOW signal. Projects, and the raising of funds for those projects.ĭisplays About the Big Ear at Outside OrganizationsĬosmic Search Magazine Online (the complete set of 13 issues)Ĭopyright © 1996-2008 Ohio State University Radio Observatory and North The group also formed an organization called "NAAPO" (North AmericanĪstroPhysical Observatory) for the purposes of developing Argus and other These is the next generation radio telescope called "Argus", which has the ability to see in all This continuing group has been exploring new possibilities. (although with a continual evolution of some people leaving and others Its destruction stayed together as a group following Big Ear's demise The volunteers who had been operating Big Ear prior to Kraus) and the many persons involved with the telescope, and to the discoveries made with that instrument.Īs was noted above, the Big Ear radio telescope was demolished by landĭevelopers in 1998. This website is meant to serve as a memorial to that unique radio telescope, to its designer and builder (the late Dr. On the nearby land owned by those developers. An adjacent 9-hole golf course wasĮxpanded into 18 holes and about 400 homes were planned for construction
Ohio Wesleyan University, Delaware, Ohio) was sold by them in 1983 to landĭevelopers who later claimed their rights to develop the land. The land on which the observatory was sitting (owned by the University Radio Observatory, with its "Big Ear" radio telescope, ceased In late 1997, after almost 40 years of operation, the Ohio State The various structures you see in the above aerial photo of Big Ear areĮach described in a separate section of this website.įor proper viewing you will need to have a browser that is both JavaScript-enabled and can handle frames. This unique probe of the depths of the cosmos was located in Delaware, Ohio (about 30 miles north of Columbus).Ĭomments About the Above Aerial Photograph of the Big Ear Radio Telescope (Search for ExtraTerrestrial Intelligence) project entered into Objects in the universe, as well as for the "Wow!" The telescope was famous for discovering some of the most distant known Big Ear covered an area larger than three football fields. Kraus, the founder and director of the observatory, who was also the designer and builder of the telescope. The Observatory was a Kraus-type radio telescope, named for Dr. Welcome to the original website of the former Ohio State University Radio Observatory (OSURO), also known as Big Ear.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
